Kidney Transplant Treatment Cost in India
Kidney Transplant or Renal Transplant is a procedure in which a person with completely failed kidneys receives a kidney from a healthy person who has both the kidneys working in good condition.
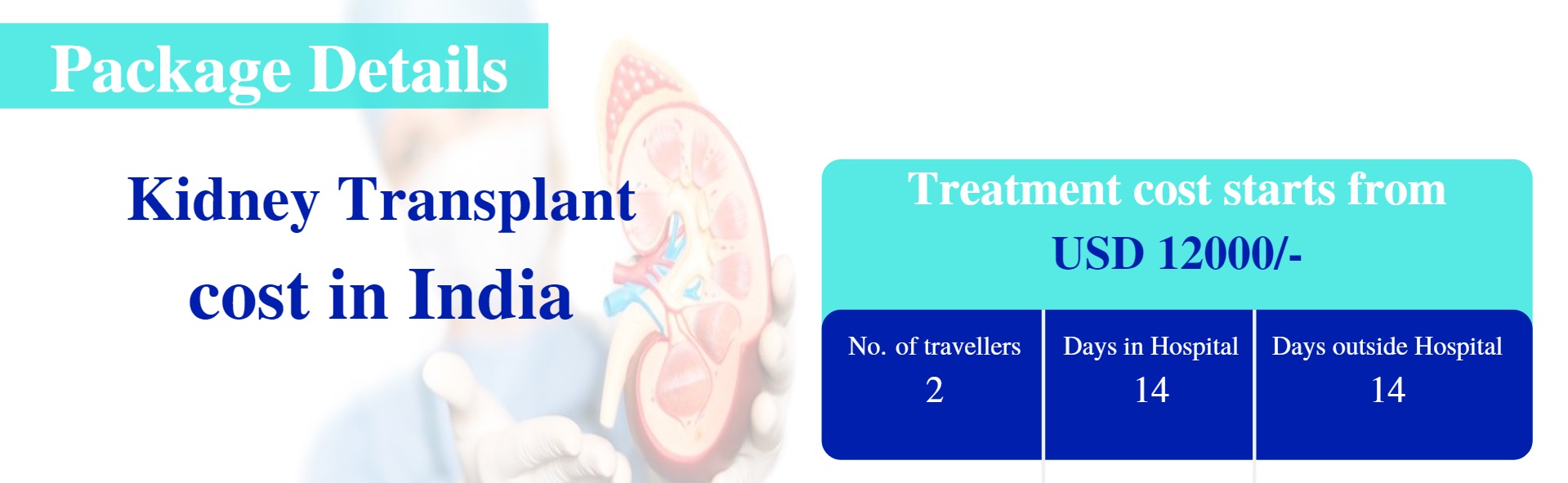
Kidney transplant surgery cost in India ranges from USD 12,000 to USD 15,000.
DOCUMENTS REQUIRED FOR KIDNEY TRANSPLANT
An affidavit from the donor stating the exact relationship with the patient & stating that donation is free, voluntary and without financial transaction & given due to love & affection only.
The cost of kidney transplant is one of the major reasons why patients decide to travel thousands of miles to get treated in India. The country boasts its high quality of medical treatment that can be available at an extremely affordable cost.
The cost of treatment may also differ from one hospital to another depending upon the infrastructure, test facilities, and surgeon, etc. Accommodation can be arranged in the hotels and guest houses located near to the hospitals and the cost may vary from USD 25-100 depending upon the patient’s choices.
Kidney Transplant Treatment Hospitals in India

Artemis Hospital
Hospital Overview Artemis Hospital, established in 2007, spread across 9 acres, is a 400 plus bed; state-of-the-art multi-speciality hospital …
Read more
Fortis, Bangalore
Hospital Overview The Fortis Hospital at Bannerghatta Road is a 276 bedded multi-speciality tertiary care hospital. It began operations in 2006 and …
Read more
BLK Speciality Hospital
Hospital Overview Dr. B L Kapur, an eminent Obstetrician and Gynaecologist, set up a Charitable Hospital in 1930 at Lahore. In 1947, he moved …
Read moreKidney Transplant
Kidney Transplant or Renal Transplant is a procedure in which a person with completely failed kidneys will receive a kidney from a healthy person who has both the kidneys working in good condition. Thus, after the surgery both the man can continue to lead a healthy and normal life. The person receiving the kidney is called a “recipient” & the person donating the kidney is called a “donor”. After the transplant, the healthy kidney (the “graft”) takes over the functions of nonworking kidneys in the recipient.
Reasons for Kidney Transplant
Kidney failure is most often a result of uncontrolled High Blood Pressure or High Diabetes. Untreated kidney failure can have a large impact on the person’s Heart and over all body functions.
- Diabetes mellitus
- High blood pressure
- Glomerulonephritis
- Polycystic Kidney Disease
- Severe anatomical problems of the urinary tract
The need for a Renal Transplant arises when a person’s kidneys have lost all their functions and the Kidneys function is being managed artificially by the help of Dialyzing Machines. Kidney transplant remains the only cure for chronic kidney disease (CKD) or end-stage renal disease (ESRD).
Causes of kidney failure
There are several causes of kidney failure, the main cause of kidney failure are other problems that have done permanent damage to the kidneys over time. The most common causes of kidney failure are chronic kidney diseases such as diabetes, uncontrolled high blood pressure and kidney inflammation (nephritis) and long term exposure to drugs and toxins. Kidney failure is the most severe stage of chronic kidney disease and also called end-stage renal disease (ESRD).
- Sudden loss of the blood flows to the kidney
- Blood or fluid loss
- Blood pressure medications
- Heart attack
- Heart disease
- Severe infection, such as sepsis
- Scarring of the liver or liver failure
- Dehydration
When kidney’s urine drainage tube (ureters) become blocked and wastes and toxins can’t leave your body
- Bladder cancer
- Blood clots in the urinary tract
- Cervical cancer
- Colon cancer
- An Enlarged prostate
- Kidney stones
- Damage to your nerves that control your bladder
- Blood clots within your urinary tract
Other causes of kidney failure are when there is direct damage to the kidneys: -
- Blood clots in the veins and arteries in and around the kidneys
- An overload of toxins from heavy metals
- Lupus, an immune system disorder that can cause inflammation of many body organs
- Scleroderma diseases affecting the skin and connective tissues
- Toxins, such as alcohol, heavy metals and cocaine
- Certain antibiotics
- Uncontrolled diabetes
Symptoms of Kidney Failure
- Reduction in amount of Urine
- Swelling of body parts such as Feet it is because of retention of fluids by failure of kidney to remove water
- Unexplained Shortness of Breath
- Excessive fatigue
- Pain in Chest
- Upset stomach, nausea, vomiting
- Feeling very itchy
- Swollen or puffy face
- Brown, red, or purple urine
Candidature for Kidney Transplantation
To undergo a kidney transplant, the recipient & donor both must be healthy &must NOT have:
1. Infections such as TB, hepatitis or osteomyelitis
2. Heart, lung, or liver disease
3. Cancer
4. In-case either the recipient or donor has any other medical issue, then they must be treated for the same first before going for the kidney transplant.
Suitable Kidney Donors
Living related donor- First family relatives of the person receiving the kidney, i.e. either of the parents, siblings, or children are preferred donors. Being related, there is an increased chance of kidney being a stronger biological “match” for the patient & thus increases the chances of being accepted in a foreign body.
Living unrelated donor
Friend or spouse can also donate. However, the recipient needs to be administered anti-rejection injections to reduce the chances of rejection of the transplanted kidney which is a foreign object in the body.
Many people worry that by donating a kidney they will become unhealthy or be in a dangerous situation. The living donor of the kidney is left with one healthy functioning kidney, which should be more than enough for the rest of the donor’s life. The donor’s activities are not usually limited.
Pre-Transplant Evaluation & Tests
Thorough investigations & evaluations of both the donor and recipient are done to ensure that the donor is perfectly healthy at the time of donation and that he /she continues to remain normal after donation. The potential recipient undergoes evaluation, adequate dialysis and is brought to an optimal state to withstand the major surgery of renal transplant.
The tests done include:
- Blood tests or skin tests to check for infections
- Heart tests such as an EKG, echocardiogram, or cardiac catheterization
- Tests to look for early cancer
- Tissue and blood typing to help make sure the body will not reject the donated kidney
Procedure for the person receiving the Kidney (Recipient)
During the procedure, the surgeon places the new kidney in the abdomen and attaches it to the artery that supplies blood to kidneys and to the vein that carries blood away from the kidney. The kidney is also attached to the ureter, which carries urine from the kidney to the bladder.
Procedure for the person donating the Kidney (Donor)
There are 3 ways by which the doctors may take out the kidney from the donor
Simple kidney removal or Open Nephrectomy
The surgeon will make an incision (cut) up to 12 inches long. This cut will be on the side, just below the ribs or right over the last ribs.
Muscle, fat, and tissue are cut and moved. The surgeon may need to remove a rib to do the procedure. The tube that carries urine from the kidney to the bladder (ureter) and blood vessels are cut away from the kidney. The kidney is then removed. Sometimes, just a part of the kidney may be removed. The cut is then closed with stitches or staples.
Radical kidney removal or Radical Nephrectomy
- The surgeon will make a cut about 8 to 12 inches long. This cut will be on the front of your belly, just below your ribs. It may also be done through the side.
Muscle, fat, and tissue are cut and moved. The tube that carries urine from the kidney to the bladder (ureter) and blood vessels are cut away from the kidney.
The kidney is then removed.
The surgeon will also take out the adrenal gland and some lymph nodes.
The cut is then closed with stitches or staples.
Laparoscopic kidney removal or Laparoscopic Nephrectomy
The surgeon will make 3 or 4 small cuts, usually no more than 1-inch each, in your belly and side. The surgeon will use tiny probes and a camera to do the surgery. - Towards the end of the procedure, the doctor will make one of the cuts larger (around 4 inches) to take out the kidney.
- The surgeon will cut the ureter, place a bag around the kidney, and pull it through the larger cut.
- This surgery may take longer than an open kidney removal. However, most people recover faster and feel less pain afterwards compared to open surgery.
- Post-Transplant Special care is taken post-surgery to minimize the risk of infection. Both the recipient & donor are closely monitored to ensure that the new organ is accepted by the body and to ensure optimum immuno suppressant medication. Post-discharge hospital stay for the recipient is usually 7-8 days &for the donor is about 5 days only.
Follow Up Care Post Kidney Transplantation:
Both the recipient & donor should take due care post-transplant & follow the medicine regime, take anti-rejection drugs as advised, have diet-lifestyle modifications & follow-up consults with the doctor as advised. The doctors will conduct regular blood and urine tests, monitor blood pressure, temperature, and urine output. Ultrasounds may be done to see if there are any abnormalities with the transplanted kidney. The period immediately following your transplant may be very stressful. Due care should be taken after your kidney transplantation surgery.
Benefits & Advantages
- No longer be bound to dialysis schedules
- Increased strength, stamina, and energy
- Lead a relatively normal lifestyle
- Have a normal diet and more normal fluid intake Anaemia, a common problem with kidney failure might be corrected after transplantation